buy all kinds of tomato disease protector at the best price
Tomato (also known as Solanum Lycopersicum) is an edible berry of a sprouting plant of the nightshade family created broadly for its consumable characteristic items
Named as a vegetable for wholesome purposes, tomatoes are an incredible source of vitamin C and the phytochemical lycopene
The normal items are commonly eaten roughly in servings of blended greens, served as a cooked vegetable, utilized as a settling of diverse organized dishes, and salted and “sun-dried” tomatoes or got dried out pounds
The history of tomatoes returns to the date of 700 A
D
possibly the origin of tomatoes starts in America where other countries began to cultivate this crop
The Spanish were the first to introduce these gorgeous red fruits (tomatoes) to Europe
Many Spaniards made living selling fresh tomatoes all over Europe
Because it was the first time anyone had seen a seemingly strange plant, the Spaniards had difficulties consuming them
They became accustomed to eating the tomato that was utilized by many cooks throughout time
As a result, tomatoes have achieved widespread acceptability and are now considered one of the most important elements in every meal
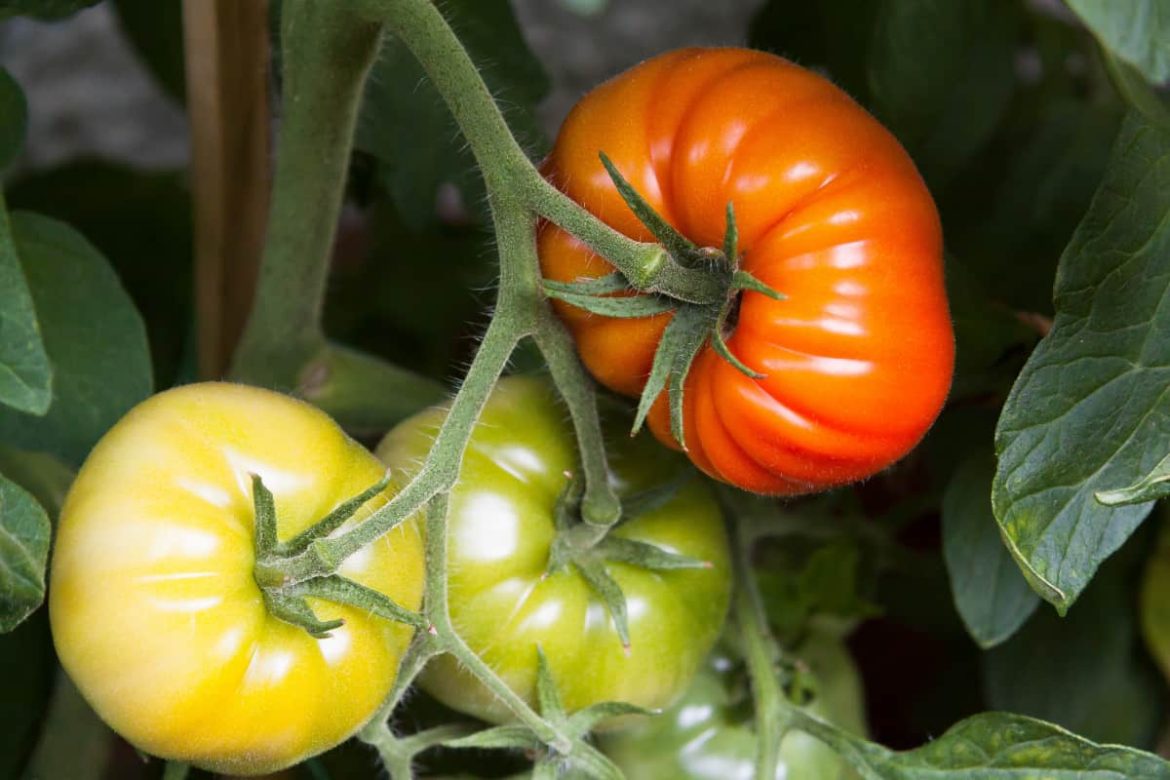
There are many various sorts of tomatoes, so we’ll look at some of the more common and popular:
Cherry tomatoes are typically red, although they can also be green, yellow, or black
They’re ideal for salads, snacking on their own, or pairing with kebabs because they’re small, spherical, and juicy
Grape tomatoes are crispier, crunchier, sweeter tasting, and have a thicker skin than cherry tomatoes
Because of their higher sugar content or possibly their appearance, they became worldwide recognized and popular in the mid-1990s
Grape tomatoes are not as juicy as cherry tomatoes, but they are equally delicious on their own or in carrot salad
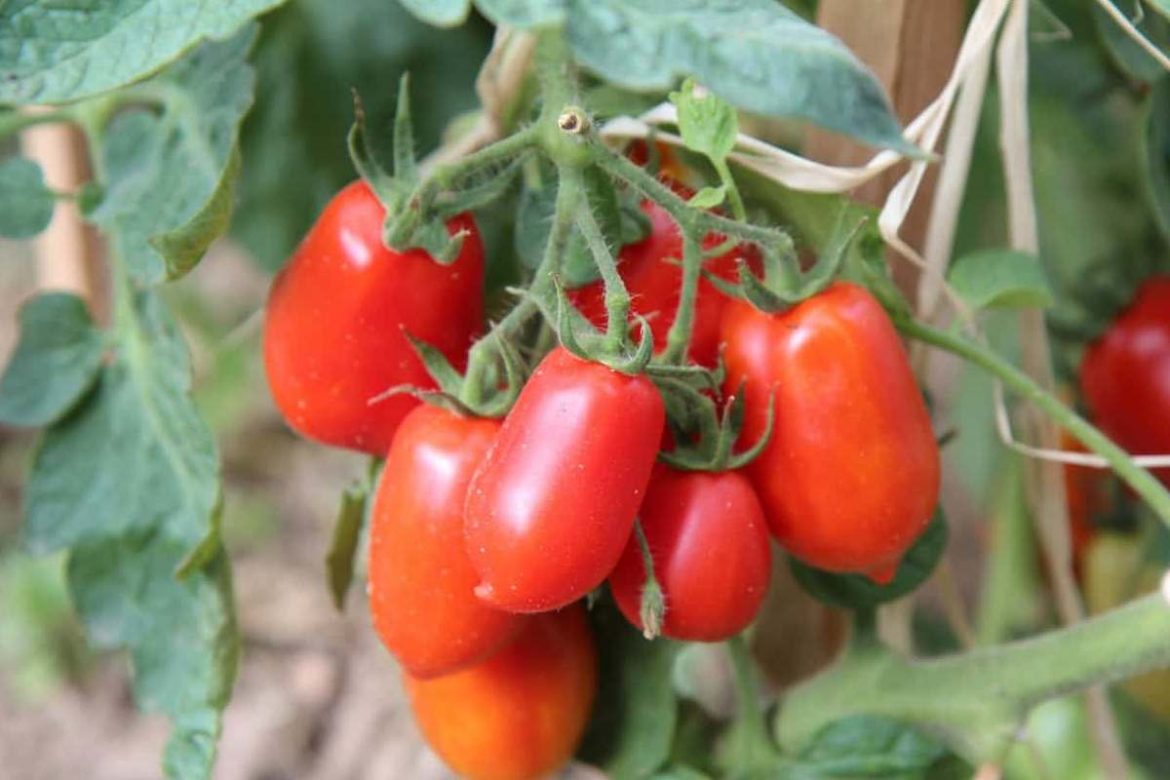
Roma tomatoes are a fantastic choice for sauces and canning since they have a pleasant flavor, are larger than cherry and grape tomato varieties, and have the shape of an egg or pear-like plum
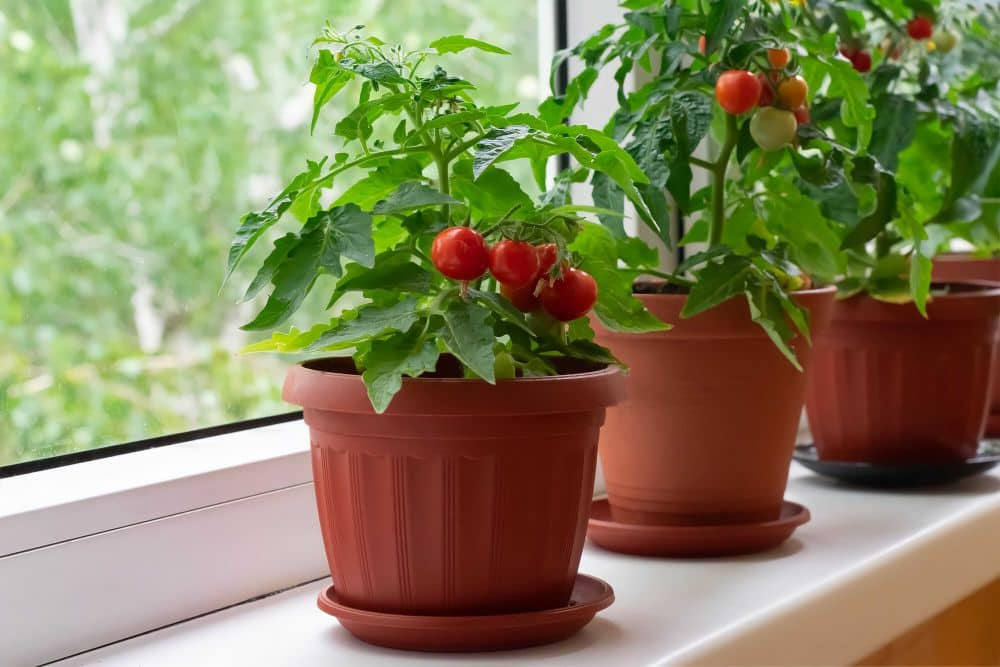
In Mississippi, tomatoes are grown commercially in both open fields and enclosed facilities (high tunnels and greenhouses)
Tomatoes are not always easy to grow, whether for commercial or personal consumption
However, a variety of maladies, insects, diseases, and pests can cause problems and destroy a crop throughout any given growing season, resulting in lower or lower-quality harvests
Tomatoes can be infected by a variety of pathogens (disease-causing organisms)
Many of the most common tomato diseases are caused by various fungi, bacteria, and viruses
A few fungus-like organisms (oomycetes), commonly known as water molds, cause illness
Tomato illnesses can be lethal if they aren’t treated quickly
Tomato diseases
Tomatoes, which belong to the genus Solanum lycopersicum, can be grown in virtually any kind of soil as long as it drains well and drains moderately
A sufficient supply of organic matter has the potential to boost yield and cut down on production issues
It is recommended that organic tomato and other closely related vegetables, such as potatoes, peppers, and eggplants, not be planted on the same plot of ground more than once every three years

In an ideal situation, any cover crop or crop that comes before tomatoes ought to be a member of the grass family
Corn is a good crop to rotate with tomatoes because it provides significant amounts of organic matter, does not encourage the growth of disease-causing organisms that attack tomatoes, and provides an excellent crop for crop rotation
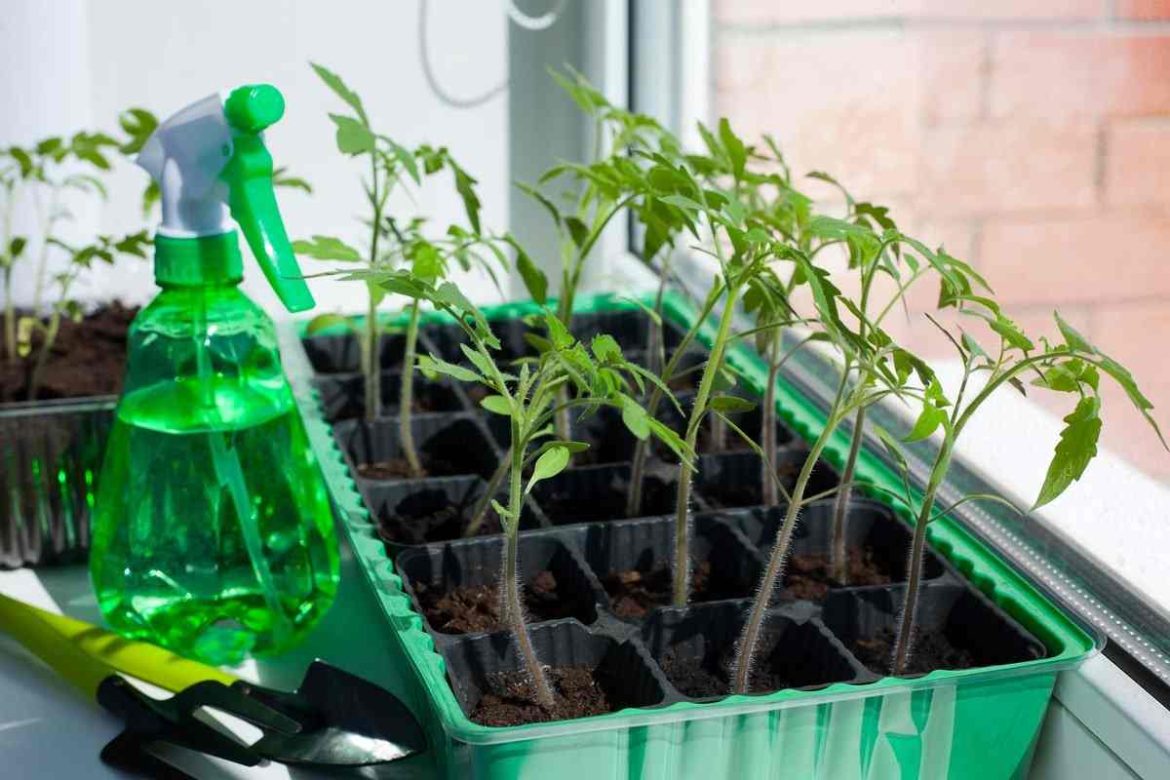
It is encouraged to utilize certified seeds and plants whenever it is possible to do so, and this should be done
Bacterial Wilt
Ralstonia solanacearum is the pathogen that is responsible for the devastating disease known as bacterial wilt or Southern bacterial blight (formerly Pseudomonas solanacearum)
This bacterium is able to live in the soil for extended periods of time and enters the roots through wounds caused by transplanting, cultivation, the damage caused by insect feeding, and natural wounds that occur when additional roots form
Both high temperatures and high levels of humidity encourage the development of disease
Within the water-conducting tissue of the plant, the bacteria reproduce very quickly, causing the tissue to become filled with slime
The plant quickly withers as a consequence of this, yet its leaves retain their green color
When an infected stem is cut lengthwise, it will have a brown appearance, and you may be able to see tiny drips of a yellowish slime
Controlling bacterial wilt of plants that have been grown in contaminated soil is tough, both in terms of prevention and treatment
Some control can be achieved by rotating sensitive plants with non-susceptible ones for a period of at least three years
Non-susceptible plants include corn, beans, and cabbage
In this particular rotation, do not include pepper, eggplant, potatoes, sunflowers, or cosmos
Eliminate and dispose of any plant material that has been contaminated
Only plants that have been verified to be disease-free should be planted

However, the cultivar Kewalo offers some resistance to bacterial wilt, despite the fact that it is not very widespread
There is currently no chemical treatment available for this illness
It is recommended that you cultivate all solanaceous plants that are vulnerable (tomatoes, peppers, eggplants, and Irish potatoes) in a separate newly prepared garden site that is completely distinct from the original garden
Before using the tiller tines and other instruments in the new garden site, you should make sure to fully rinse off any soil that was on them from the previous infested location
In recent times, a number of bacterial wilt resistant rootstocks for grafted tomato, bell pepper, and eggplant plants have been investigated, and the results have shown that these rootstocks have a high level of resistance
There is a possibility that grafted plants are accessible
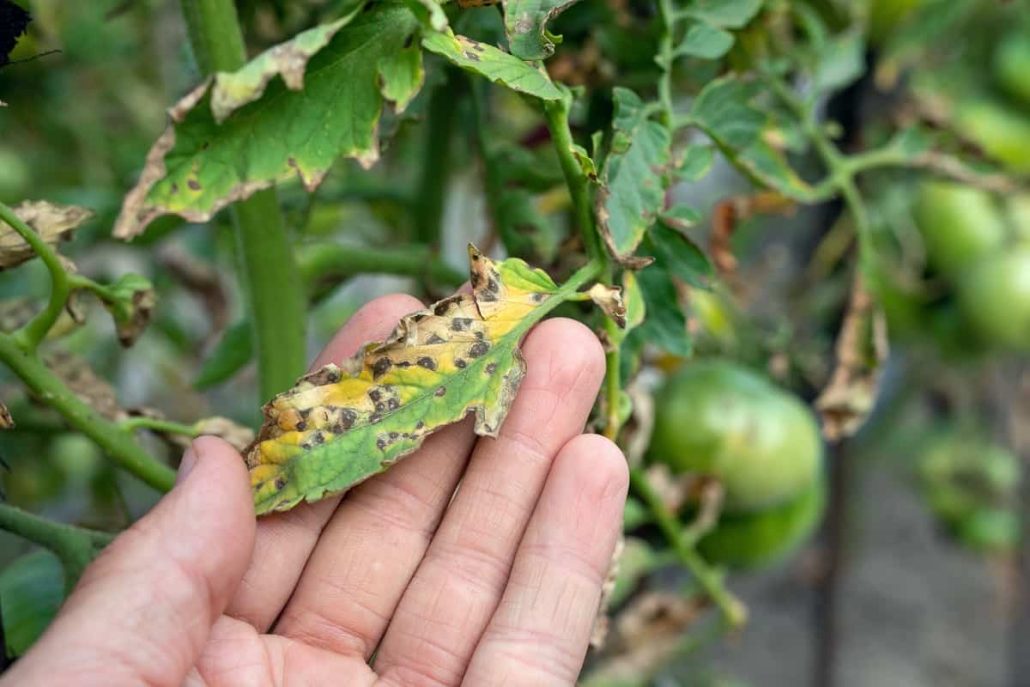
Bacterial Spot
This disease is brought on by several different species of the bacteria Xanthomonads, but the one responsible for it most often is Xanthomonads perforans
It only affects green tomatoes, not red ones
Additionally, peppers have the disease
During the rainy seasons, the disease tends to be more widespread
Spots on the leaves and fruits of the plants have caused damage to them, which in turn has led to decreased yields, defoliation, and sun scalded fruit
The symptoms include numerous small, water-soaked spots ranging from angular to irregular shapes on the leaves, and patches ranging from slightly raised to scabby in appearance on the fruits
It’s possible that the specks on the leaf have a yellow halo
The centers become dry and brittle, and they often tear
The bacteria are able to survive the winter on tomato plants that have volunteered themselves as well as on plant detritus that has been infected
The presence of moisture in the air promotes the growth of disease
The majority of the reported cases of the sickness can be linked back to the intense downpours that occurred in the region

The infection of leaves takes place through the leaf’s naturally occurring apertures
Insects or other kinds of mechanical injury are required for disease transmission to take place in fruits
Once it has taken hold in a field, bacterial spot is notoriously tough to eradicate
Any type of water movement from one leaf or plant to another, such as splashing rains, overhead watering, or touching or handling wet plants, has the potential to spread bacteria from infected plants to healthy plants
Use only seeds and plants that have been verified to be free of the illness
Both for prevention and treatment
Steer clear of any locations that have tomatoes or peppers planted in them the previous year
If possible, use drip or furrow irrigation rather than watering from above
Remove and dispose of any plant material that is infected with the illness
Prune plants to enhance air circulation
Spraying with a copper fungicide will provide a level of control over the bacterial disease that is satisfactory
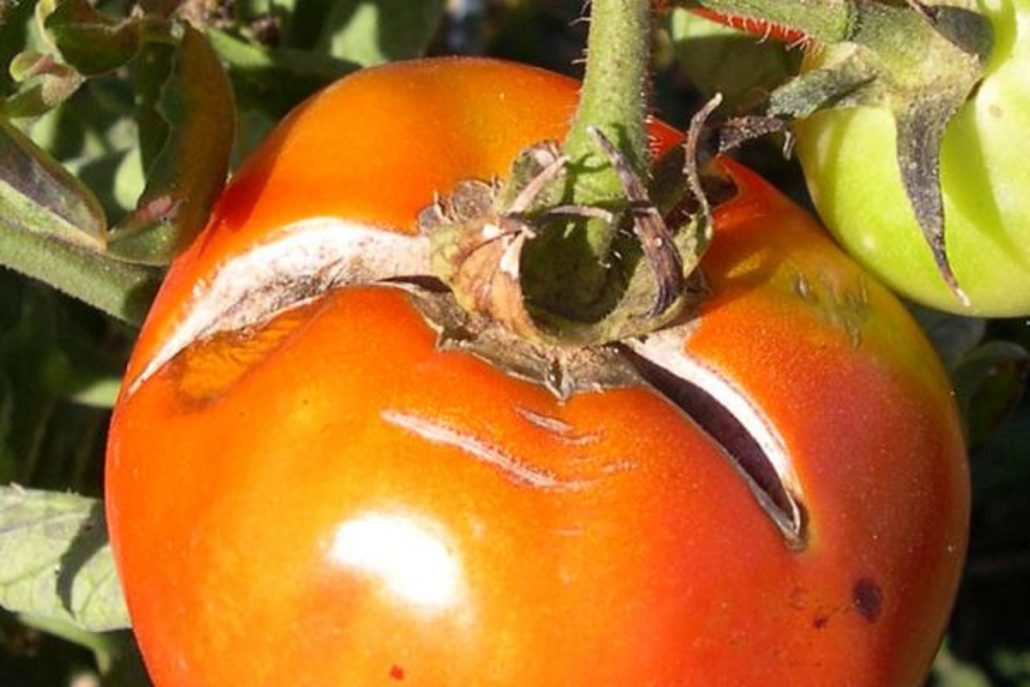
Tomato Pith Necrosis
The disease known as tomato pith necrosis typically manifests itself early in the growing season and affects greenhouse and high tunnel tomato output
On the other hand, tomato pith necrosis can infect tomatoes and peppers in home food gardens when spring weather is cool and wet
This condition typically occurs in tomatoes

Pith necrosis is brought on by a number of different kinds of soil-borne Pseudomonas bacteria, the most common of which being Pseudomonas corrugata, in addition to Pectobacterium carotovorum
These bacteria are regarded to be weak pathogens that infect fast growing tomato plants when environmental circumstances are cloudy, chilly, and damp
Signs and Symptoms: The initial sign of this disease is the appearance of necrotic, or blackened, regions on the stems of the plant
These areas may first occur near to the leaf petioles
The charred patches come together to form a band that runs along the stem of the plant and extends out onto the leaf petioles
After an infection of the leaf petiole has taken place, certain parts of the leaf blades may also get darkened
As the condition advances, the bacteria will eventually infect the interior of the stems, which may result in the stem splitting
The pith, which is located inside the stem, may become segmented or laddered, and the stem itself may shrink and split
After some time, the interior of the stems will turn hollow
Because of the damage to the stem, the upper parts of the tomato plant no longer receive their normal supply of water, which causes the upper leaves to become yellow and the shoots to wilt
Another symptom is the creation of a large number of adventitious roots that spring forth from bigger stems
These roots can be found everywhere on the plant
However, this type of root growth on stems also occurs with tomato bacterial canker and as a result of damage caused by spray drift exposure to dicamba, which is a fairly common broadleaf weed pesticide that is used on lawns
Both of these conditions can cause the stems to get infected
The symptom, which appears as a greasy and water-soaked patch on the blossom end of the developing green fruit, may or may not be present
This area is located near the stem end of the fruit
This symptom of the fruit is extremely like to those of two additional illnesses known as late blight and buckeye rot of tomato, respectively
By submitting a plant sample to the local Extension office, you can determine which disease is damaging the tomato crop and take preventative measures
The plant material will be submitted, for a fee, to the Clemson Plant and Pest Diagnostic Clinic in order to receive a diagnosis and suggestions for its management
Plants may be able to recuperate when the temperature turns warmer, and the rapid growth that occurs in the spring may slow down
When watering the garden, do not use an overhead irrigation method; instead, water the soil at the base of the plants using drip irrigation, soaker hoses, or by hand with a garden hose

To ensure that there is sufficient moisture in the soil for the plant to recuperate, the frequency of irrigation should be increased
However, if plants are found to have pith necrosis, all diseased parts of the plant, including the roots, should be carefully removed and discarded
The severity of this disease is increased when excessive nitrogen fertilization is applied during the early stages of the growing season
The suggestions for fertilizing should be followed based on the findings of the soil test
Within the vegetable garden, implement a crop rotation strategy that spans three years due to the fact that bacteria that live in the soil can survive there until the following growing season
In the future, make sure to leave a distance of three feet between each tomato plant in the garden
This will boost air circulation around the plants, which will in turn hasten the drying of any dew or rainwater that has fallen on the foliage
Plant according to the spring planting dates
It is best to postpone planting until later in the spring when conditions are more favorable
There are no therapies that can be sprayed on to lessen illness
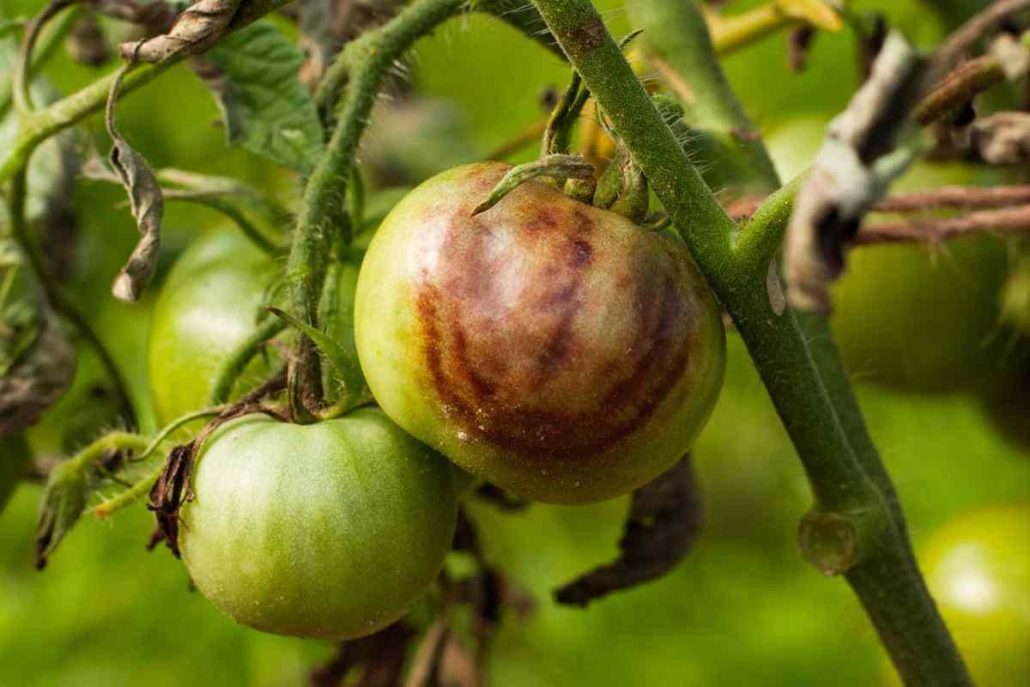
what is tomato blight
The deadly illness known as tomato blight, which may completely destroy an entire crop of tomatoes, can be prevented or treated using these tomato blight treatments
If you walk into a room full of gardeners and use the word “blight,” you can expect to hear a lot of grunts and grumbles from them
When a tomato patch is infected with a common fungal disease, it can methodically destroy the plant by damaging the tissue of the leaves, stems, and fruits
This illness is caused by fungi
The blight can be harmful if it is not treated, but tomato farmers can take prompt action to combat the disease
Fungal spores are what cause blight to spread, and they do so by being carried from infected plants by animals, wind, water, and insects, and then being left behind on soil
Since the progression of the disease is dependent on moisture, it can only occur when fungal spores in the soil are exposed to moisture in the form of dew or rain

When it rains, water strikes the ground, and this causes dirt and spores to be splashed onto the lower leaves of plants
This is where the disease first manifests itself in the plant
Despite the fact that blight on plants and in the soil cannot be cured, there are a few straightforward approaches that may be taken to manage this disease
What does tomato blight look like? The fungus that causes tomato blight infects the tomato plant and can manifest itself in a number of different ways
“In the early stages of late tomato blight, the bottom leaves are the first to show symptoms, which appear as black rings caused by powdery blight
According to Tammy Sons of Tennessee Wholesale Nursery, this causes the leaves to change from a light emerald green to a musty yellow in color and look

“The leaves will finally become so diseased that they will fall off
” As the blight travels up the stalk of the tomato vine, it causes brown spots to appear on the tomatoes, and eventually the entire plant is infected with it
According to Tammy, “End-stage blight causes the entire tomatoes to rot as a result of the blight infection
”
Different kinds of blight
Early Onset of Blight
This disease is caused by the fungi Alternaria linariae, which was formerly known as A
solani
when this disease first appears on plants, it appears as minute, brown lesions that are concentrated primarily on the older foliage
The spots become larger, and in the middle of the infected area, you could notice a pattern of concentric rings that looks like a bull’s eye
It’s possible that the tissue around the spots will turn yellow
If conditions of excessive temperature and humidity persist throughout this time, a significant portion of the plant life will perish
The lesions that appear on the stems are quite similar to those that appear on the leaves and can girdle the plant if they appear close to the ground (collar rot)
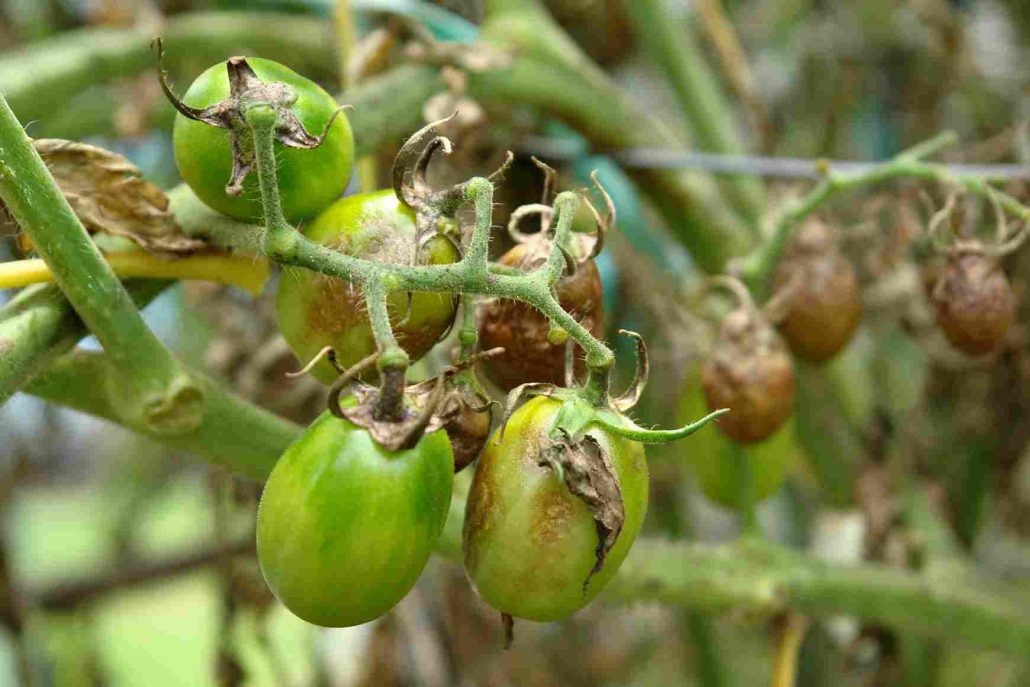

Lesions on the fruit can grow to be quite large and will typically cover almost the whole surface area of the fruit
On the surface of the fruit are clearly visible concentric rings
The infection causes the fruit to frequently fall off
The fungus can live on infected waste in the soil, on seed, on tomato plants that have grown on their own, and on other solanaceous hosts such Irish potato, eggplant, and black nightshade (a common, related weed)
Treatment and Preventative Measures: Utilize tomato cultivars that are resistant to the disease or tolerant of its effects
Utilize seed that is free of pathogens, and don’t transplant sick plants into the ground
Make use of crop rotation, get rid of weeds and tomato plants that have grown on their own, leave enough space between plants so that they don’t touch, mulch plants, fertilize properly, and make sure that irrigation water doesn’t get tomato foliage wet
This will help the plants continue to grow healthily
Remove and discard infected lower branches and leaves by trimming them off
To lessen the severity of a disease, get the garden soil tested once a year and make sure it has an adequate supply of potassium
The findings of the soil test will determine how much lime to add to the ground
Calcium nitrate should be applied to tomato plants once every month to ensure healthy growth
Choose one of the following fungicides if the disease is severe enough to require the use of chemical control: mancozeb (very good); chlorothalonil or copper fungicides (good)
Always make sure you follow the instructions on the label
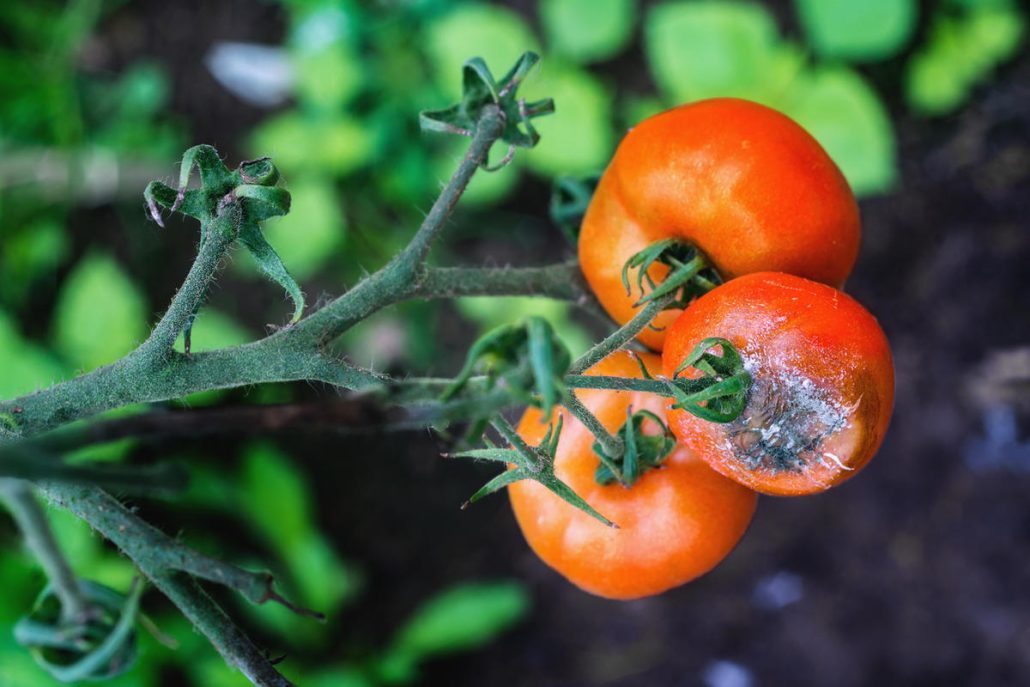
Late Blight
The fungus Phytophthora infestans, which lives in water mold, is responsible for the potentially devastating disease known as late blight, which affects potatoes and tomatoes
The late blight is at its most destructive when the weather is cool and moist
This virus is capable of infecting every component of the plant
Lesions on young leaves are typically rather tiny and have the appearance of black, water-soaked patches
These spots on the leaves will immediately become larger, and on the lower surface of the leaves, a white mold will begin to emerge around the margins of the affected area
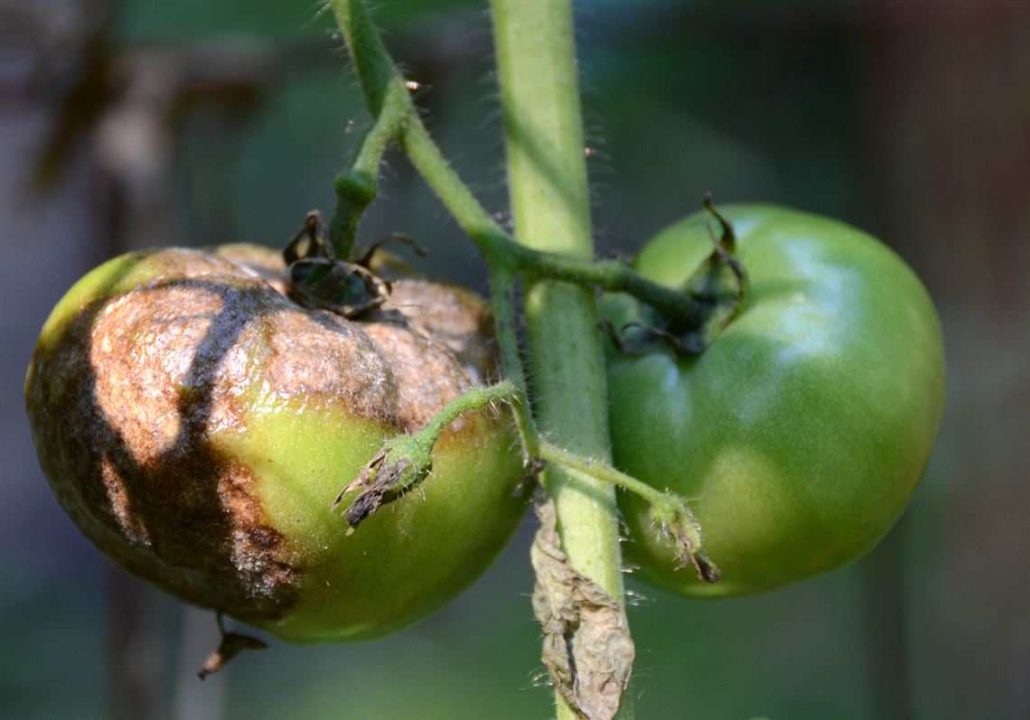

Within 14 days of the first signs, the plant may completely defoliate, which is characterized by a browning and shriveling of the leaves and stems
Lesions that are glossy, black, or olive-colored form on infected tomato fruits, and they can cover considerable parts of the fruit
Rainwater and wind can carry fungal spores from plant to plant and from garden to garden
When coupled with high levels of humidity, daytime temperatures in the upper 70s of Fahrenheit are excellent for the spread of infection
How to prevent the occurrence of tomato blight?
Make sure the tomato plants are kept dry
It is essential to trim foliage and side-shoots to maximize air movement and ensure the evaporation of surface moisture, as explained by Simon Crawford
“Environmental control must focus on reducing the likelihood of leaves remaining wet for an extended period,” he says
“This means trimming foliage and side-shoots
” Therefore, educate yourself on the right techniques for pruning tomato plants
Keep plants adequately ventilated
If you are growing tomato plants in a greenhouse or polytunnel, it is important to ensure that these spaces have adequate ventilation so that they do not become overly humid
To grow tomatoes well outside, choose a location that gets plenty of air circulation
Tie up or stake plants
Either keep the leaves of bush tomato plants off the earth by staking them or enhance air circulation by routinely tying up cordon tomato plants with soft string
Bush tomato plants can be staked

According to Simon Crawford, avoiding a dense clump of foliage on bush kinds planted in pots can be accomplished by trimming the plants and partially supporting them with a bamboo cane
As the fruits develop, remove the bottom leaves from the plant
This not only prevents the leaves from being wet from the soil, but it also improves air circulation and hastens the ripening of the tomatoes by exposing them to the most possible sunlight
The morning is the best time to water tomato plants
This is done so that the plants do not remain damp all through the night
It is important to simply hydrate the soil, and not the foliage or plants themselves
Place your tomato plants in an area that is free of pests and diseases
Never plant tomatoes in soil or compost that has previously been used for plants that were infected with a disease
It is possible for the spores that cause tomato blight to survive in the soil for up to four years
Practise good plant hygiene
Composting dead plants in an appropriate manner is of the utmost significance, and in order to limit the risk of infection in gardens and allotment plots, “plant dumps” must be eradicated
According to the advice of Simon Crawford, a plot should have as many old potatoes removed as feasible
Rotate crops
It is important to remember that potatoes and tomatoes should not be grown in the same soil from year to year
tomato allergy
Tomatoes are one of the most widely consumed fruits in the world and may be utilized for a number of different things due to their versatility
Tomatoes of all kinds, including wild varieties, can be found growing in a wide range of geographic locales
Because of the wide variety of nutrients that they contain, they are utilized both in their natural and processed forms of consumption
On the other hand, it is common knowledge that tomatoes can cause allergic reactions in people who are predisposed to having them

There is a strong correlation between grass pollinosis and tomato allergies, as well as other food and allergy related conditions
Oral Allergy Syndrome (OAS), urticaria, dermatitis, systemic responses, rhinitis, stomach pain, and anaphylaxis are some of the major clinical symptoms that can occur in tomato allergy sufferers
People who are allergic to tomatoes should avoid eating tomatoes and should also avoid coming into touch with tomato products in order to avoid an allergic reaction
Different kinds of responses to tomato
Mucosal irritation-Tomato has been implicated in an array of adverse reactions, including uncomfortable mucosal irritation due to acidic pH
When touched, the tomato plant has the potential to trigger a sort of allergic contact dermatitis that manifests as a rash or itching on the skin
The symptoms of oral allergy syndrome often include itching in the mouth as well as swelling of the lips and tongue
People who are allergic to grass pollen may have signs of oral allergy syndrome when they eat tomatoes
This is not a real allergy to tomatoes; rather, it is a cross reactivity of the proteins in tomatoes to the pollen in grass
The treatment consists of either cooking the fruit or avoiding it altogether
Celery, kiwi, melon, and peaches are some examples of other foods that fall into the same category
Anaphylaxis manifests itself with a variety of symptoms, including hives, swelling, asthma, coughing, vomiting, diarrhea, and low blood pressure

This is a result of degranulation of IgE mast cells
Because of this, responses to tomato might take on a variety of shapes
A physician who specializes in allergy treatment can assist in determining the nature of the reaction that a patient is having to tomato and in doing the proper tests to confirm or refute a clinical allergy diagnosis
Tomato allergies are exceedingly uncommon, which is somewhat surprising given that tomatoes and products made from tomatoes are among the foods that are consumed the most frequently in western diets
Someone who is sensitive to tomatoes is also likely to have allergic reactions to other nightshades, such as potatoes, tobacco, and eggplant
In most cases, the symptoms of a tomato allergy manifest themselves not long after the allergen has been consumed
They are as follows: rash, eczema, or hives on the skin (urticaria) coughing, sneezing, wheezing, or runny nose diarrhea swelling of the face, mouth, tongue, or throat (angioedema)
tomato leaf problems
If you’ve ever tried growing tomatoes before, you’re undoubtedly already familiar with the various issues that might arise with tomato leaves
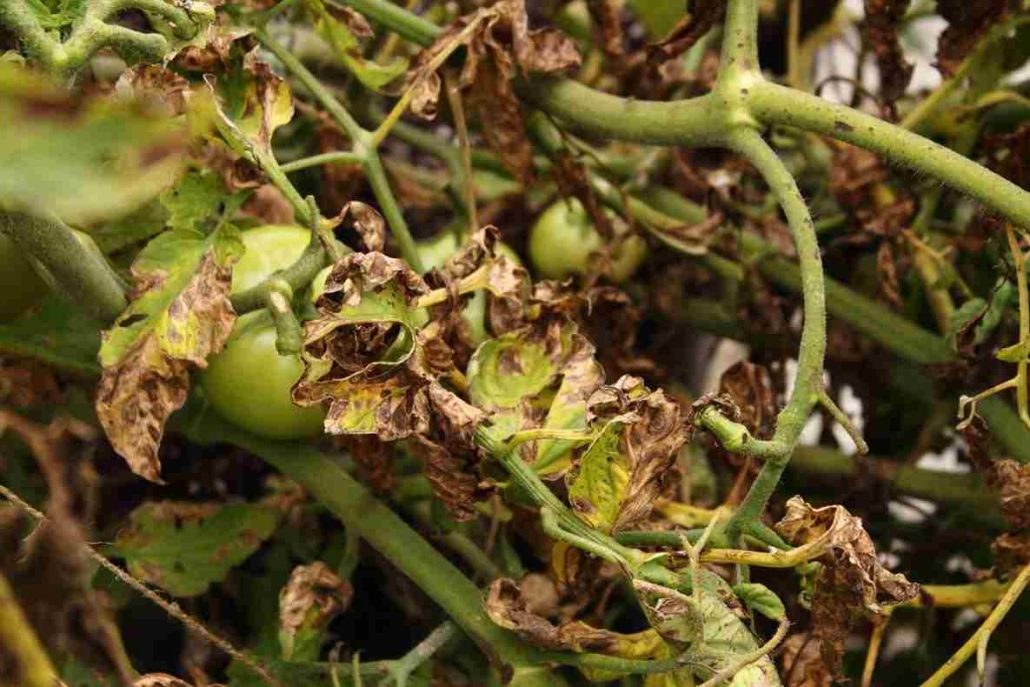
It’s possible that you’ve discovered that the leaves on your tomato plant are turning yellow, brown, or spotted
The question now is, what causes these issues with the tomato plant? The terrible truth is that tomatoes are quite vulnerable to a wide variety of illnesses and insects
And a good number of them result in blotches of yellow or brown on the tomato leaves
Simply examining the leaves of the plant can frequently be sufficient to identify the root of the problem
The distinct pattern of yellowing or spotting on your tomato plant will provide you with a wealth of information about the specific disease or pest that is wreaking havoc on your plant
Make use of this guide to tomato leaf problems to assist you in determining what the issue is and what, if anything, can be done about it
When the leaves on your plant appear yellow but the plant itself is in good health, you should initially experiment with fertilizing it with an organic liquid fertilizer
Because liquid fertilizer is absorbed more quickly, you should begin to see improvements within a day or two of applying it
If you observe that the new leaves on your plant, which are located at the top of the plant, are yellow with green veins, you may have an iron shortage
You should make sure that the pH of your soil falls somewhere between 6 and 6
8
You should be suspicious of a potassium deficiency if the older leaves, which are the ones at the bottom of the plant, have yellow margins and green veins

It is possible that you are suffering from a zinc shortage if you observe dark dots within the yellow areas and the leaves are small and narrow
Calcium shortage may be the cause of your tomato plant’s young leaves appearing yellow and the growth tips withering away
A lack of nitrogen can be identified by stunted plant growth as well as a general yellowing of the plant’s leaves
Before adding anything to the soil other than organic fertilizer and compost, it is best practice to get the soil tested to determine whether or not it is deficient in any nutrients
Diseases related to tomato leaves: The list below are several common tomato leave diseases:
Alternaria Canker
Bacterial Canker
Bacterial Speck
Early Blight
Gray Leaf Spot
Late Blight









